Cloud Hosting vs VPS: Which Should You Choose?
Choosing a web hosting plan used to be simple. You started with shared hosting, and when your site grew, you bought a dedicated server. But the landscape has changed. Now, the middle ground is dominated by two powerful options: Cloud Hosting and Virtual Private Servers (VPS).
For business owners and website administrators, the choice between these two can be confusing. Both offer better performance than shared hosting. Both provide dedicated resources. Yet, they operate on fundamentally different architectures, and choosing the wrong one could lead to unnecessary costs or website crashes during critical traffic spikes.
If you are trying to decide where to house your website or application, you need to look beyond the marketing jargon. This guide breaks down the differences, pros, cons, and costs of Cloud Hosting versus VPS, helping you make the right infrastructure decision for your specific needs.
What Is Cloud Hosting?
To understand cloud hosting, you have to stop thinking about a “server” as a single physical box sitting in a room. Instead, think of cloud hosting as a network.
Definition and core concept
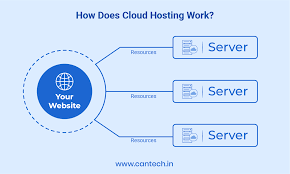
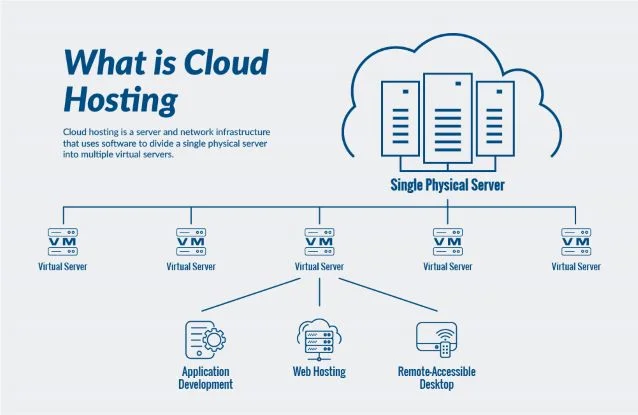
Cloud hosting utilizes a cluster of servers working together to store your data and run your website. Rather than relying on one machine, your website taps into a vast pool of computing resources (CPU, RAM, and storage) spread across multiple physical servers.
If one server in the cluster experiences a hardware failure, another immediately takes over. This architecture eliminates single points of failure, making cloud hosting incredibly resilient.
How cloud infrastructure works
Imagine a power grid. When you plug in a lamp, you aren’t drawing electricity from one specific generator; you are drawing from the entire grid. Cloud hosting works similarly. A layer of virtualization software sits on top of the physical servers, creating a “cloud” of resources.
When you host a site here, you are allotted a portion of these resources. Crucially, because the resources are virtualized across many machines, you can expand them instantly. If your website suddenly goes viral, you can tap into more power from the grid without needing to physically upgrade hardware.
Typical cloud hosting use cases
Because of its flexibility and redundancy, cloud hosting is the go-to choice for:
- High-traffic websites: Sites that receive millions of visitors and cannot afford downtime.
- Streaming services: Platforms like Netflix that require immense bandwidth and storage.
- Viral content publishers: News sites or blogs where traffic can jump from zero to 100,000 visitors in an hour.
- Mission-critical apps: Business tools that must remain online 24/7.
What Is VPS Hosting?
VPS stands for Virtual Private Server. While it sounds similar to cloud hosting because it also uses virtualization, the underlying structure is more traditional.
Virtual Private Server explained
A VPS mimics the environment of a dedicated server within a shared hosting environment. Technically, it is still one physical server. However, the hosting provider uses hypervisor software to slice that physical server into several smaller, private compartments.
Each compartment is a VPS. It runs its own operating system (OS) and has dedicated resources (RAM, CPU, and disk space) that are reserved solely for you.
How VPS differs from shared hosting
In standard shared hosting, you are not just sharing the physical server; you are sharing the resources. If a neighbor on your shared server uses too much RAM, your site slows down.
With a VPS, your “slice” of the server is protected. Even if other users on the same physical machine are running heavy processes, your allocated CPU and RAM remain yours. It offers the stability of a dedicated server at a fraction of the price.
Common VPS use cases
VPS hosting is the logical next step for websites that have outgrown shared hosting but don’t need the infinite scale of the cloud. It is ideal for:
- Small to medium business websites: Sites with steady, predictable traffic.
- Agency portfolios: Professional sites that need consistent performance.
- Private game servers: Hosting a Minecraft or Counter-Strike server for friends.
- Development environments: Programmers needing a sandbox to test code before going live.
Cloud Hosting vs VPS: Key Differences
At a glance, both options give you a private environment and dedicated resources. However, the operational differences are significant.
Performance
Resource allocation
In a VPS environment, your resources are capped. If you pay for 4GB of RAM, you have exactly 4GB of RAM. It is located on one specific physical machine. If that machine is under heavy load, performance can occasionally fluctuate, though reputable providers minimize this.
Cloud hosting allocates resources from a pool. Because the load is balanced across many servers, performance tends to be more consistent. If the physical hardware hosting your data gets busy, the cloud infrastructure can route your processing requests to a freer node in the cluster.
Handling traffic spikes
This is the biggest differentiator. A VPS has a “hard ceiling.” If your website traffic exceeds what your 2 CPU cores and 4GB of RAM can handle, your site will slow down or crash.
Cloud hosting handles spikes effortlessly. Because the resources are virtual, the system can temporarily allocate more power to your site to handle the rush (often called “bursting”), keeping your site online during viral moments.
Scalability
Auto-scaling vs manual scaling
Cloud hosting defines scalability. Many cloud plans offer “auto-scaling.” You can set parameters so that if your CPU usage hits 80%, the system automatically adds more CPU power. When traffic drops, it scales back down.
VPS scaling is usually manual. If you need more RAM, you often have to upgrade your plan. This might involve a migration to a larger server or a reboot of your current virtual machine, resulting in temporary downtime.
Growth flexibility
If you are planning for massive growth, cloud is the winner. You can start small and grow to enterprise-level capacity without ever migrating servers. With a VPS, there is a limit to how large you can grow before you maximize the physical server’s capacity and have to move to a dedicated machine.
Pricing
Pay-as-you-go vs fixed plans
VPS hosting typically uses a fixed monthly pricing model. You pay $20 a month for a specific set of specs, regardless of whether you use them or not. This makes budgeting very easy.
Cloud hosting often operates on a usage-based or “pay-as-you-go” model. You pay for the hours your server is running, the gigabytes of bandwidth you transfer, and the storage you occupy.
Cost predictability
VPS offers high cost predictability. Your bill is the same every month. Cloud hosting can be unpredictable. If you have a massive traffic spike, your hosting bill for that month will increase to reflect the extra resources used.
Reliability & Uptime
Redundancy and failover
Cloud hosting is designed for high availability. If a stick of RAM fails in a physical server within the cloud cluster, your site doesn’t go down; it simply shifts to healthy hardware. This redundancy is built-in.
Single-server limitations
A VPS resides on a single physical server. If the motherboard on that specific server dies, your VPS goes down until the hosting company fixes the hardware. While reliable, it lacks the automatic failover capabilities of the cloud.
Control & Customization
Server access levels
Both VPS and Cloud hosting usually provide “root access” (for Linux) or Administrator access (for Windows). This means you have total control over the software stack. You can install any software, change security settings, and configure the OS however you like.
Configuration freedom
There is a slight learning curve for both. However, VPS environments often act more like traditional computers, which can be more familiar to system administrators. Cloud environments might require specialized knowledge of the provider’s dashboard (like AWS Console or Google Cloud Platform) to manage networking and storage effectively.
Pros and Cons of Cloud Hosting
Pros
- High Scalability: Effortlessly handle traffic surges without crashing.
- Better Uptime: Hardware failures rarely result in website downtime due to redundancy.
- Flexible Pricing: You only pay for what you use, which can be cheaper for sporadic workloads.
- Speed: Load balancing ensures your site remains fast even under pressure.
Cons
- Variable Monthly Costs: It can be difficult to predict exactly what your bill will be at the end of the month.
- More Complex Pricing Models: Understanding bandwidth costs and egress fees can be confusing for beginners.
- Security Configuration: While the infrastructure is secure, the user is often responsible for securing the virtual environment, which can be complex.
Pros and Cons of VPS Hosting
Pros
- Predictable Pricing: A flat monthly fee makes financial planning simple for small businesses.
- Full Server Control: Root access allows for deep customization of the server environment.
- Simple Setups: Often easier for beginners to understand as it mimics a standard computer.
- Dedicated Resources: You don’t compete with neighbors for CPU or RAM.
Cons
- Limited Scalability: You cannot instantly add resources during a traffic spike.
- Single Point of Failure: If the physical server fails, your site goes down.
- Resource Waste: You pay for the server capacity even when your traffic is low or zero.
Cloud Hosting vs VPS: Use Case Comparison
To help you decide, let’s look at specific scenarios.
| Scenario | Recommended Option | Why? |
|---|---|---|
| Small Business Website | VPS | Traffic is likely steady and predictable. The fixed cost helps with budgeting, and you don’t need infinite scaling. |
| E-commerce Store | Cloud | During sales (like Black Friday), traffic can spike 10x. The cloud scales to keep the store open, preventing lost sales. |
| SaaS Web App | Cloud | Apps require high availability. The redundancy of the cloud ensures users can always log in. |
| Development & Testing | VPS | Developers need a consistent environment to test code. A VPS is a cheap, isolated sandbox perfect for this. |
Which Should You Choose in 2026?
As technology advances, the line between these two services is blurring, but the core advice remains consistent.
When cloud hosting is the better choice
Choose cloud hosting if your primary goal is reliability and growth. If you are launching a startup that you hope will explode in popularity, or if you run an online store where downtime literally costs you money, the cloud is necessary. The slightly higher complexity and variable pricing are insurance premiums you pay for keeping your site online no matter what happens.
When VPS hosting makes more sense
Choose VPS hosting if your primary goal is control and budget stability. If you are running a blog, a corporate informational site, or a personal project where a standardized monthly bill is essential, VPS is the superior choice. It offers a massive performance upgrade over shared hosting without the confusing billing of the cloud.
FAQs – Cloud Hosting vs VPS
Is cloud hosting better than VPS?
“Better” depends on your needs. Cloud hosting is better for reliability and scalability (handling traffic spikes). VPS hosting is generally better for budget predictability and simpler management for steady, lower-traffic sites.
Which is cheaper: cloud or VPS?
For entry-level usage, VPS is often cheaper because plans start at very low flat rates (e.g., $5–$10/month). Cloud hosting can be cheaper for sporadic tasks where you can turn the server off when not in use, but generally, high-performance cloud environments cost more than comparable VPS setups.
Can I migrate from VPS to cloud hosting?
Yes. Most hosting providers make it relatively easy to migrate. If you start on a VPS and your site outgrows it, you can move your files and database to a cloud environment. However, it does require some technical knowledge regarding server configuration and DNS.
Is cloud hosting more secure than VPS?
Both are secure, but cloud hosting often has better physical security and data redundancy (backups). However, the security of the actual website depends on you. If you have weak passwords or outdated software, both Cloud and VPS are equally vulnerable to hacking.
Which option is best for beginners?
Managed VPS is often the best middle ground for beginners. “Managed” means the hosting company handles the technical updates and security, giving you the power of a VPS without the headache of being a system administrator. Unmanaged cloud hosting can be overwhelming for a complete novice.
Making the Final Infrastructure Decision
The battle between Cloud Hosting and VPS isn’t about one technology replacing the other; it is about choosing the right tool for the job.
In 2026, the decision ultimately comes down to your tolerance for risk and your budget structure. If you demand a flat monthly fee and have steady traffic, a VPS will serve you faithfully for years. But if you demand 100% uptime and the ability to scale from ten visitors to ten million overnight, the cloud is the only architecture that can keep up with your ambition.
Assess your current traffic, your technical skills, and your wallet. The right choice is the one that lets you sleep at night, knowing your website is running smoothly.