Shared Hosting vs VPS vs Cloud Hosting: Key Differences Explained
Choosing the right web hosting plan can feel like navigating a maze without a map. You encounter technical terms like “uptime,” “bandwidth,” and “scalability,” often without a clear explanation of what they mean for your specific situation. The most common confusion, however, usually boils down to three main choices: Shared Hosting, VPS, and Cloud Hosting.
These three options form the backbone of the web hosting industry, yet they serve very different purposes. Making the wrong choice early on can lead to slow loading speeds, security vulnerabilities, or paying for resources you don’t actually need. Conversely, selecting the right environment ensures your site runs smoothly, scales as you grow, and stays within budget.
This guide breaks down the mechanics, pros, and cons of each hosting type. We will strip away the jargon to help you understand exactly how your website data is stored and delivered to visitors. Whether you are launching a personal blog or managing a high-traffic e-commerce store, understanding these differences is the first step toward building a successful online presence.
What Is Shared Hosting?
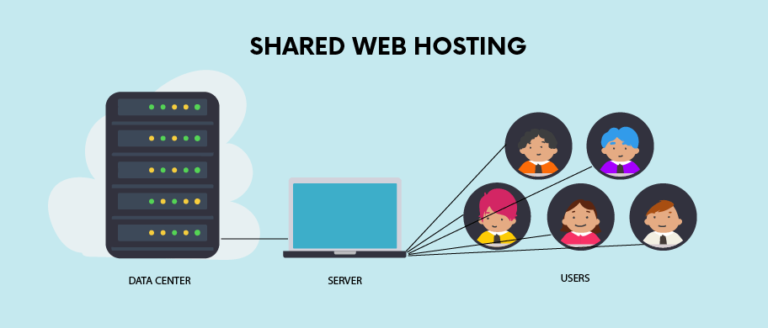
Shared hosting is the entry-level option for most websites. It is often compared to living in a college dormitory or a large apartment complex. You have your own private room (your website), but you share common resources like water, electricity, and the building’s entrance with everyone else.
Simple definition
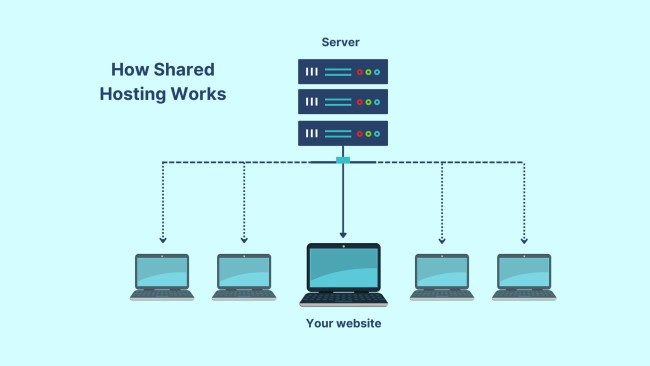
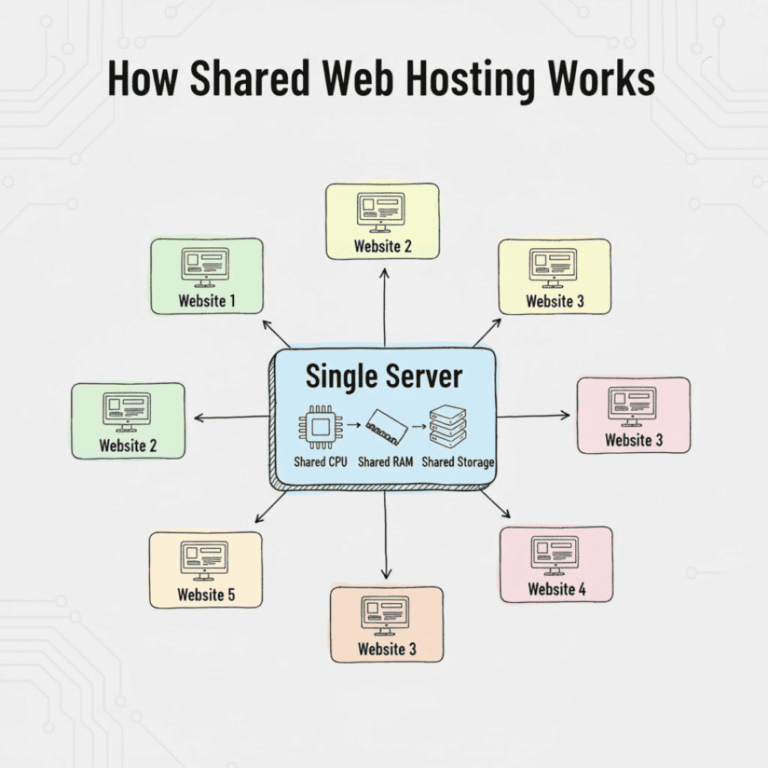
In technical terms, shared hosting means multiple websites reside on a single physical server. All the sites on that server draw from a collective pool of resources, including CPU power, memory (RAM), and disk space.
How shared hosting works
When you sign up for a shared hosting plan, the provider allocates a directory on a server for your website files. The server software manages requests for hundreds, sometimes thousands, of different websites simultaneously. Because the costs of maintaining the server are split among many users, this is almost always the most affordable option.
However, the “shared” nature creates a “noisy neighbor” effect. If another website on your server suddenly receives a massive spike in traffic or runs a faulty script that hogs the CPU, your website might slow down as a result. Hosting providers use software to try and limit this, but it remains an inherent risk of the environment.
Who shared hosting is best for
This setup is ideal for:
- Personal blogs and portfolios: Sites with low to moderate traffic volume.
- Small business websites: Informational sites that don’t require heavy processing power.
- Beginners: Users who want a “set it and forget it” solution where the host manages all technical server maintenance.
What Is VPS Hosting?
VPS stands for Virtual Private Server. If shared hosting is a dorm room, VPS hosting is like owning a condo in a high-rise building. You still share the physical structure (the server) with others, but you have your own dedicated unit with guaranteed resources that no one else can touch.
What “virtual private server” means
A VPS uses virtualization technology to split one powerful physical server into multiple isolated virtual servers. Although other users are present on the same hardware, their activities do not impact your performance.
How VPS hosting works
A hypervisor (software that creates and runs virtual machines) creates a virtual barrier between users. When you purchase a VPS plan, you are guaranteed a specific amount of RAM, CPU cores, and storage space. Even if the server is busy, your slice of the pie is reserved exclusively for you.
This isolation also allows for greater customization. Unlike shared hosting, where you are stuck with the server configurations the host chooses, a VPS often gives you “root access.” This means you can install specific software, change security settings, and configure the operating system to your exact needs.
Key benefits of VPS hosting
- Reliability: Your resources are guaranteed, eliminating the “noisy neighbor” problem.
- Customization: You have more control over the server environment.
- Better Security: The virtual separation ensures that if another site on the physical server is compromised, your site remains safe.
What Is Cloud Hosting?
Cloud hosting is the modern evolution of web hosting. It breaks away from the traditional model of relying on a single physical machine. Instead, imagine renting a massive, interconnected network of computers that work together as one.
Cloud hosting explained in simple terms
Cloud hosting utilizes a cluster of servers—the “cloud”—to host your website. Your data isn’t stored on just one piece of hardware. Instead, it is replicated across multiple machines. If one server fails or undergoes maintenance, another one instantly takes over, ensuring your site stays online.
How cloud hosting works
The architecture of cloud hosting is designed for redundancy and flexibility. The resources you use—processing power, memory, and storage—are pulled from the entire network. This structure allows for “on-demand” scaling. If your website goes viral overnight, you can instantly tap into more resources from the cloud cluster to handle the load, often with just a few clicks or even automatically.
Why cloud hosting is popular
- Uptime: Since you aren’t dependent on one single point of failure (one server), cloud hosting offers superior uptime.
- Scalability: You can scale resources up or down in real-time based on demand.
- Pay-as-you-go: Many cloud providers charge you only for the specific resources you consume, similar to a utility bill, rather than a flat monthly fee.
Shared Hosting vs VPS vs Cloud Hosting: Quick Comparison
To help visualize the differences, here is a quick breakdown of how these three hosting types stack up against key criteria.
| Feature | Shared Hosting | VPS Hosting | Cloud Hosting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | Low ($2 – $10/mo) | Medium ($20 – $100/mo) | Variable ($10 – $500+/mo) |
| Performance | Basic; can fluctuate | High; guaranteed resources | High; excellent uptime |
| Scalability | Limited | Moderate; requires upgrade | Excellent; instant scaling |
| Resource Allocation | Shared with others | Dedicated slice of server | Dedicated & distributed |
| Technical Skill | Low (Beginner friendly) | Medium/High (Root access) | Medium/High |
Performance Differences Explained
The speed at which your website loads is critical for both user experience and search engine rankings.
Speed and resource limits
In a shared environment, your speed is capped by the limits of the shared server. If the server is overcrowded, your Time to First Byte (TTFB) will suffer. VPS hosting solves this by giving you dedicated RAM and CPU. Your site loads consistently fast because those resources are always waiting for your command. Cloud hosting often offers the best performance of all because it can leverage a vast network of high-speed servers to deliver content efficiently.
How traffic spikes are handled
This is often the dealbreaker for growing sites. If a shared hosting site gets a traffic spike (like from a viral social media post), the host might temporarily throttle the site or even take it offline to protect other users on the server. A VPS can handle more traffic, but it still has a hard ceiling based on your plan limits. Cloud hosting shines here; it can absorb massive traffic surges by dynamically adding resources, keeping your site live when it matters most.
Reliability and uptime
Hardware failures happen. On shared and VPS hosting, if the physical motherboard or drive fails, your site goes down until the hardware is fixed. Cloud hosting mirrors your data across different devices. If Node A fails, Node B picks up the slack immediately, often without you even noticing a blip in service.
Cost Comparison: Which Is Most Affordable?
Budget is often the primary deciding factor for new website owners.
Shared hosting pricing
Shared hosting is incredibly cheap because providers pack many customers onto one server. You can often find promotional rates as low as $2 or $3 per month. However, renewal rates usually jump higher (often double or triple the intro rate), so always read the fine print.
VPS hosting pricing
VPS is a mid-tier option. Managed VPS hosting (where the host handles updates and patches) generally costs between $30 and $50 per month. Unmanaged VPS plans, where you handle the technical upkeep, can be cheaper, sometimes starting around $5 to $10 per month, but they require significant technical expertise.
Cloud hosting pricing
Cloud pricing models vary. Some providers offer flat-rate monthly plans similar to VPS. Others, like AWS or Google Cloud, use a usage-based model where you pay for every hour of CPU time and gigabyte of bandwidth used. While this can be cost-effective for efficiency, it can also lead to unpredictable bills if you don’t monitor your usage closely.
Long-term cost considerations
While shared hosting is cheap upfront, the hidden cost is performance. A slow site loses customers. If your business relies on website revenue, the extra $20/month for a VPS or Cloud plan often pays for itself in retained sales and better user engagement.
Scalability and Growth Potential
Scalability refers to how easily your hosting plan can grow with your business.
Why scalability matters
Migrating a website to a new server is a complex task that can involve downtime. Ideally, you want a host that allows you to upgrade seamlessly as your traffic grows.
Which hosting type scales best
Cloud hosting is the undisputed king of scalability. You can add more RAM or CPU power instantly without restarting your server. Shared hosting is the worst; once you outgrow the shared environment, you must migrate to a completely different server type (usually a VPS). VPS hosting sits in the middle; you can usually upgrade to a larger tier, but it may require a server reboot to allocate the new resources.
When to upgrade
If your shared hosting site starts loading slowly during peak hours, or if you receive warnings from your host about exceeding resource limits, it is time to move to VPS or Cloud.
Ease of Use and Technical Requirements
Not everyone is a server administrator. Your technical comfort level should play a big role in your decision.
Beginner-friendly options
Shared hosting is designed for non-technical users. It almost always comes with a control panel like cPanel or Plesk, allowing you to manage emails, databases, and files with a graphical interface. The host manages security patches and server software updates.
Server management responsibilities
With unmanaged VPS and pure Cloud environments, you are often handed a blank server with a command-line interface. You are responsible for installing the web server (like Apache or Nginx), PHP, and security firewalls.
Learning curve comparison
If you don’t know how to use an SSH terminal, stick to Shared Hosting or look specifically for “Managed” VPS or Cloud hosting. Managed plans cost more but provide the same user-friendly support and control panels as shared hosting.
Security Differences Between Hosting Types
Security is paramount, especially if you handle sensitive user data or payment information.
Shared environment risks
The main risk in shared hosting is cross-contamination. While rare, sophisticated attacks can sometimes bypass directory permissions. If a hacker compromises one site on the server, they might be able to impact others. Additionally, if another user’s IP address gets blacklisted for spamming, your email deliverability might suffer because you share that IP.
VPS isolation benefits
The virtualization layer in VPS hosting adds a robust security boundary. Even if a neighbor gets hacked, your virtual container remains secure. You also have a dedicated IP address, protecting your sender reputation.
Cloud security features
Cloud hosting providers often invest heavily in enterprise-grade firewalls and DDoS protection. Because your data is distributed, physical theft or damage to a single data center won’t result in total data loss. However, the complexity of configuring cloud security groups can lead to vulnerabilities if not managed correctly.
Which Hosting Type Is Right for You?
Still undecided? Here is a breakdown based on typical use cases.
Personal blogs and small websites
If you are starting a blog, a local business page, or a hobby site, Shared Hosting is sufficient. It is affordable and easy to use. You can always upgrade later if your site takes off.
Growing business websites
For small e-commerce stores, professional portfolios, or business sites with consistent daily traffic, VPS Hosting is the sweet spot. It offers the reliability and speed professional businesses need without the complexity of enterprise cloud setups.
High-traffic or global websites
If you run a large e-commerce platform, a SaaS application, or a media site with fluctuating viral traffic, Cloud Hosting is the best choice. The ability to scale instantly ensures you never miss a sale due to downtime.
Shared Hosting vs VPS vs Cloud Hosting for SEO
Google has confirmed that page speed is a ranking factor.
Speed and uptime impact
Slow websites rank lower. Because shared hosting is prone to slowdowns during peak times, it can negatively impact your SEO efforts compared to the consistent speed of VPS or Cloud. Furthermore, frequent downtime (common with low-quality shared hosts) signals to Google that your site is unreliable, which can hurt your search visibility.
Hosting quality and rankings
While hosting alone won’t make you rank #1, bad hosting can prevent you from ranking at all. A VPS or Cloud solution provides the solid technical foundation—fast TTFB and high reliability—that allows your content and keywords to perform their best.
Choosing the right option for SEO
If SEO is a priority and you have the budget, skip shared hosting. The performance gains from VPS or Cloud give you a competitive edge in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Frequently Asked Questions
Is VPS better than shared hosting?
Yes, in terms of performance, security, and control. However, it is more expensive and may require more technical knowledge unless you choose a managed plan.
Is cloud hosting worth the extra cost?
For mission-critical websites where downtime equals lost revenue, absolutely. For hobby sites, the extra cost is likely unnecessary.
Can I switch hosting types later?
Yes. Most hosting providers offer free migration services to help you move from a shared plan to a VPS or Cloud plan as your site grows.
Which hosting is best for beginners?
Shared hosting is the best starting point because it is low-risk, low-cost, and requires zero technical maintenance.
Final Verdict: Shared Hosting vs VPS vs Cloud Hosting
The hosting landscape doesn’t have to be confusing. It essentially comes down to where you are in your website’s lifecycle.
- Start with Shared Hosting if you are launching a new site with a limited budget and low traffic expectations. It allows you to focus on content creation rather than server management.
- Move to VPS Hosting once your site gains traction, you start selling products, or you notice performance slowdowns. This is the logical middle ground for established businesses.
- Choose Cloud Hosting if you need maximum uptime, handle unpredictable traffic spikes, or run a complex application that demands enterprise-level scalability.
The smartest strategy is often to start small and scale up. Don’t overpay for a Ferrari when a sedan will get you to the grocery store. Monitor your site’s performance, listen to your users, and upgrade your infrastructure only when your growth demands it.