Cloud Hosting vs Traditional Hosting in 2026: Pros, Cons & Which Is Better
Choosing the right web hosting infrastructure is one of the most critical decisions for any digital business, developer, or content creator. In 2026, the landscape of the internet has evolved significantly. With the rise of AI-driven applications, heavier media content, and an expectation for instantaneous page loads, the infrastructure supporting your website matters more than ever.
The debate between cloud hosting vs traditional hosting isn’t just about terminology; it’s about fundamental differences in how your data is stored, served, and scaled. While traditional hosting—comprising shared, VPS, and dedicated servers—has been the backbone of the web for decades, cloud hosting has rapidly become the standard for modern agility.
Understanding these differences is crucial because the wrong choice can lead to site crashes during traffic spikes, security vulnerabilities, or simply overpaying for resources you don’t use. This guide provides a comprehensive, unbiased comparison of cloud hosting and traditional hosting, helping you decide which architecture aligns best with your goals in 2026.
What Is Cloud Hosting?
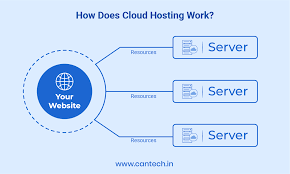
Cloud hosting is a method of hosting websites on virtual servers that pull their computing resource from extensive underlying networks of physical web servers. It follows the utility model of computing: you pay for what you use, and the resources are available on demand.
Architecture Overview
Unlike traditional hosting, which relies on a single server (or a partition of one), cloud hosting utilizes a cluster architecture. Your website’s data is replicated across multiple storage devices. If one server in the cluster fails, another instantly takes over, ensuring zero downtime. This virtualization layer abstracts the software from the hardware, allowing for fluid movement of data and resources.
Key Benefits of Cloud Hosting
- High Availability: The distributed nature means hardware failure doesn’t result in site failure.
- On-Demand Scalability: You can add RAM or CPU power instantly without rebooting or migrating to a new server.
- Load Balancing: Traffic is distributed across multiple network interfaces, preventing bottlenecks during peak times.
Keywords: cloud hosting explained, scalable cloud hosting
What Is Traditional Hosting?
Traditional hosting refers to the classic model where your site resides on a specific physical server. This category generally splits into three main types: Shared Hosting, Virtual Private Servers (VPS), and Dedicated Servers.
Shared, VPS, and Dedicated Explained
- Shared Hosting: You share a single physical server and its resources (CPU, RAM, bandwidth) with hundreds or thousands of other websites. It is cost-effective but susceptible to the “noisy neighbor” effect, where another site’s traffic spike slows down your site.
- VPS (Virtual Private Server): A physical server is split into several virtual compartments. You still share hardware, but you have dedicated portions of resources and better isolation than shared hosting.
- Dedicated Hosting: You rent an entire physical server. You have total control and access to all resources, but you are also responsible for all maintenance, and scalability is limited to the physical capacity of that machine.
Limitations
The primary limitation of traditional hosting is its dependence on single-point hardware. If the physical server degrades, needs maintenance, or fails, your site goes down. Furthermore, scaling usually requires a manual migration to a larger server, causing downtime and administrative headaches.
Keywords: traditional web hosting, shared hosting explained
[Compare Hosting Plans]
Performance Comparison
In the cloud hosting vs traditional hosting debate, performance is often the deciding factor for high-traffic sites.
Load Speed and Latency
In a traditional dedicated environment, raw processing power can be incredibly high because there is no virtualization overhead. For predictable, stable workloads, a dedicated server often offers the best raw input/output operations per second (IOPS).
However, cloud hosting in 2026 has largely closed this gap. Modern cloud infrastructure uses bare-metal cloud instances that offer the speed of dedicated servers with the flexibility of the cloud. Furthermore, cloud environments are typically optimized for faster data transfer rates across their internal networks.
Resource Allocation
Traditional shared hosting struggles with resource contention. If a neighboring site goes viral, your page load speed suffers. Cloud hosting isolates resources more effectively. Even if a node in the cloud cluster is under heavy load, the system can migrate your container to a healthier node automatically, preserving your site’s speed.
Keywords: cloud hosting performance, traditional hosting speed
Scalability & Flexibility
This is where the two types of hosting diverge most drastically.
Auto Scaling in the Cloud
Cloud hosting is defined by elasticity. In 2026, most premium cloud providers offer “auto-scaling.” This allows you to set parameters—for example, “if CPU usage exceeds 70%, add 2GB of RAM.” The system adjusts automatically during a traffic spike and scales back down when traffic subsides. This is crucial for eCommerce sites running flash sales or news sites covering breaking stories.
Vertical Scaling in Traditional Hosting
Traditional hosting is rigid. Scaling a dedicated server means physically installing more RAM or migrating to a new machine. This process can take hours or days and almost always involves scheduled downtime. While VPS hosting allows for some vertical scaling, you are eventually capped by the physical limits of the host machine.
Keywords: scalable hosting comparison, cloud hosting auto scaling
Reliability & Uptime
Uptime is the metric that keeps business owners awake at night.
Redundancy
Cloud hosting is built on redundancy. Your data is mirrored. Storage Area Networks (SANs) ensure that even if a hard drive melts down, your data remains accessible from another drive in the array. This architecture allows cloud providers to offer uptime guarantees (SLAs) often exceeding 99.99%.
Failover
Traditional hosting has a single point of failure. If the motherboard on your dedicated server fails, your business is offline until a technician physically replaces the part. While RAID configurations in traditional servers help with drive failures, they do not protect against motherboard or power supply unit failures in the same way a cloud cluster does.
Keywords: cloud hosting uptime, reliable hosting comparison
[View Cloud Hosting Deals]
Security & Compliance
Security in 2026 is complex, dealing with sophisticated DDoS attacks and automated vulnerability scanners.
Isolation and Protection
Cloud hosting providers invest heavily in perimeter security. They typically include advanced Web Application Firewalls (WAF) and DDoS protection at the network edge. Because the environment is virtualized, if a security breach occurs in one container, it is easier to isolate and quarantine than on a shared server where an exploit could theoretically compromise the root directory.
Backup Automation
Traditional hosting usually requires you to manage your own backups or pay for an add-on service. Cloud hosting makes snapshots and backups incredibly easy—often automated daily or hourly. Disaster recovery in the cloud is faster because you can spin up a new instance from a saved image in minutes.
However, traditional dedicated servers can offer a strict form of data sovereignty and isolation that certain highly regulated industries (like banking or healthcare) might prefer for compliance reasons, ensuring data never leaves a specific physical drive.
Keywords: secure cloud hosting, traditional hosting security
Cost & Pricing Model Comparison
The pricing structures of these two models are fundamentally different.
Cloud: Pay-as-you-go
The cloud offers an operational expenditure (OpEx) model. You pay for the CPU hours, bandwidth, and storage you actually consume.
- Pros: Cost-efficient for variable traffic. You don’t pay for idle resources.
- Cons: Unpredictable bills. A massive traffic spike or a coding error that causes a memory leak can lead to “bill shock” at the end of the month.
Traditional: Fixed Plans
Traditional hosting is a capital expenditure (CapEx) or fixed subscription model. You pay a flat monthly fee for a set amount of resources.
- Pros: Predictable budgeting. You know exactly what the bill will be.
- Cons: You pay for capacity you don’t use during quiet periods, and you pay expensive overage fees if you exceed limits.
| Feature | Cloud Hosting Cost | Traditional Hosting Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Billing Model | Pay-as-you-go / Hourly | Fixed Monthly / Yearly |
| Startup Cost | Low (start small) | Medium to High (Dedicated) |
| Predictability | Low (varies with usage) | High (flat fee) |
| Value | Best for fluctuating traffic | Best for stable, predictable traffic |
Keywords: cloud hosting pricing, hosting cost comparison
Control, Customization & Management
How much technical expertise do you have?
Root Access and Customization
Dedicated servers (Traditional) offer the ultimate level of control. You have root access to the kernel. You can configure the server environment exactly how you want it, which is ideal for legacy applications with specific dependencies.
Cloud hosting also offers root access (in IaaS models), but you are often interacting with a hypervisor layer. For most users, this difference is negligible, but for deep system architects, the “bare metal” access of a dedicated server is sometimes preferred.
Managed Services
Both hosting types offer “Managed” variations. Managed Cloud Hosting is increasingly popular in 2026, where the provider handles the OS updates, security patching, and scaling configurations, allowing you to focus solely on your application code.
Keywords: hosting control level, managed hosting comparison
[Check Traditional Hosting Pricing]
Global Performance & CDN Integration
The internet is global, and latency depends on physical distance.
Multi-region Deployment
Cloud hosting providers (like AWS, Google Cloud, Azure, and specialized providers) have data centers in dozens of regions globally. With a few clicks, you can deploy your application in New York, London, and Tokyo simultaneously.
CDN Integration
While you can use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) with traditional hosting, cloud hosting is often natively integrated with CDNs. This pushes your static content (images, CSS, JavaScript) to edge servers around the world, ensuring that a user in Australia loads your site just as fast as a user in the US. Traditional hosting makes this multi-region architecture difficult and expensive to replicate.
Keywords: global cloud hosting, CDN hosting benefits
Best Use Cases for Each Hosting Type
To summarize the cloud hosting vs traditional hosting decision, here is where each excels:
When to Choose Cloud Hosting
- eCommerce Stores: You need auto-scaling to handle Black Friday sales without crashing.
- SaaS Applications: You need high availability and easy global deployment.
- Startups: You need to start small with low costs but have the ability to scale infinitely if you go viral.
- High-Traffic Media Sites: You need redundancy to ensure content is always available.
When to Choose Traditional Hosting
- Small Local Businesses: A simple brochure site with predictable traffic works perfectly on Shared or VPS hosting.
- Regulatory Compliance: Industries requiring specific hardware isolation (though dedicated cloud instances exist, traditional dedicated servers are the classic solution).
- Budget Blogs: If you are just starting and budget is the only concern, shared traditional hosting is the cheapest entry point.
- Legacy Apps: Applications designed for specific hardware environments.
Keywords: best hosting for small business, best hosting for ecommerce
Pros & Cons Summary Table
| Feature | Cloud Hosting | Traditional Hosting (Dedicated/VPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Instant, often automated | Slow, manual, requires downtime |
| Reliability | High (Redundant hardware) | Moderate (Single point of failure) |
| Performance | High (Load balanced) | High (Raw power, but constrained) |
| Cost | Variable (Pay for use) | Fixed (Predictable) |
| Security | Advanced (Perimeter defense) | Standard (Server-level defense) |
| Management | User-friendly dashboards | Requires technical admin skills |
FAQs – Cloud Hosting vs Traditional Hosting
Is cloud hosting better than traditional hosting?
For most modern applications, yes. Cloud hosting offers better reliability, scalability, and flexibility. However, traditional dedicated hosting can still be superior for specific, stable, high-performance workloads where raw processing power is required at a fixed cost.
Is cloud hosting more expensive?
It depends on usage. For a low-traffic site, cloud hosting can be more expensive than cheap shared hosting. However, for a high-traffic site, cloud hosting is often more cost-effective than buying a massive dedicated server that sits 90% idle during off-peak hours.
Which hosting is more reliable?
Cloud hosting is generally more reliable due to its decentralized nature. If one server fails, the cloud cluster automatically reroutes traffic to a healthy server. Traditional hosting relies on single hardware components, making it more prone to downtime.
Can I migrate from traditional hosting to cloud hosting?
Yes. Most cloud providers offer migration tools or managed migration services. Moving from a traditional cPanel shared host to a cloud environment is a standard procedure in 2026.
Is cloud hosting faster than shared hosting?
Almost always. Shared hosting suffers from resource contention. Cloud hosting provides dedicated resources and better network infrastructure, resulting in faster Time to First Byte (TTFB) and overall page load speeds.
Which hosting type is best for beginners?
Managed Cloud Hosting is often best for beginners because it removes the complexity of server management while providing the benefits of the cloud. Standard shared hosting is also beginner-friendly but lacks performance.
Does cloud hosting improve SEO?
Indirectly, yes. Search engines prioritize page speed and uptime (Core Web Vitals). Because cloud hosting generally offers superior speed and nearly 100% uptime, it provides a solid foundation for better search rankings compared to unreliable traditional hosting.
Conclusion
The battle of cloud hosting vs traditional hosting in 2026 is largely being won by the cloud, driven by the need for speed, uptime, and scalability. The ability to weather traffic storms and pay only for what you use aligns perfectly with the modern digital economy.
However, traditional hosting—particularly high-end dedicated servers—remains a viable, powerful option for businesses with predictable workloads and specific hardware requirements.
If your priority is growth, agility, and global reach, the cloud is the clear winner. If your priority is raw power at a fixed, predictable budget for a stable workload, traditional dedicated hosting still holds the crown.
Ready to upgrade your infrastructure?